-
Partial Information Decomposition
Multimodal machine learning is a fast-growing subarea of artificial intelligence research that aims to develop systems capable of integrating and fusing many heterogeneous modalities. Partial information decomposition (PID) has emerged as a useful information-theoretic framework to quantify the degree to which individual modalities independently, redundantly, or synergistically convey information about a target variable. New algorithms and frameworks are proposed to estimate PID accurately and efficiently on high-dimensional multimodal data.
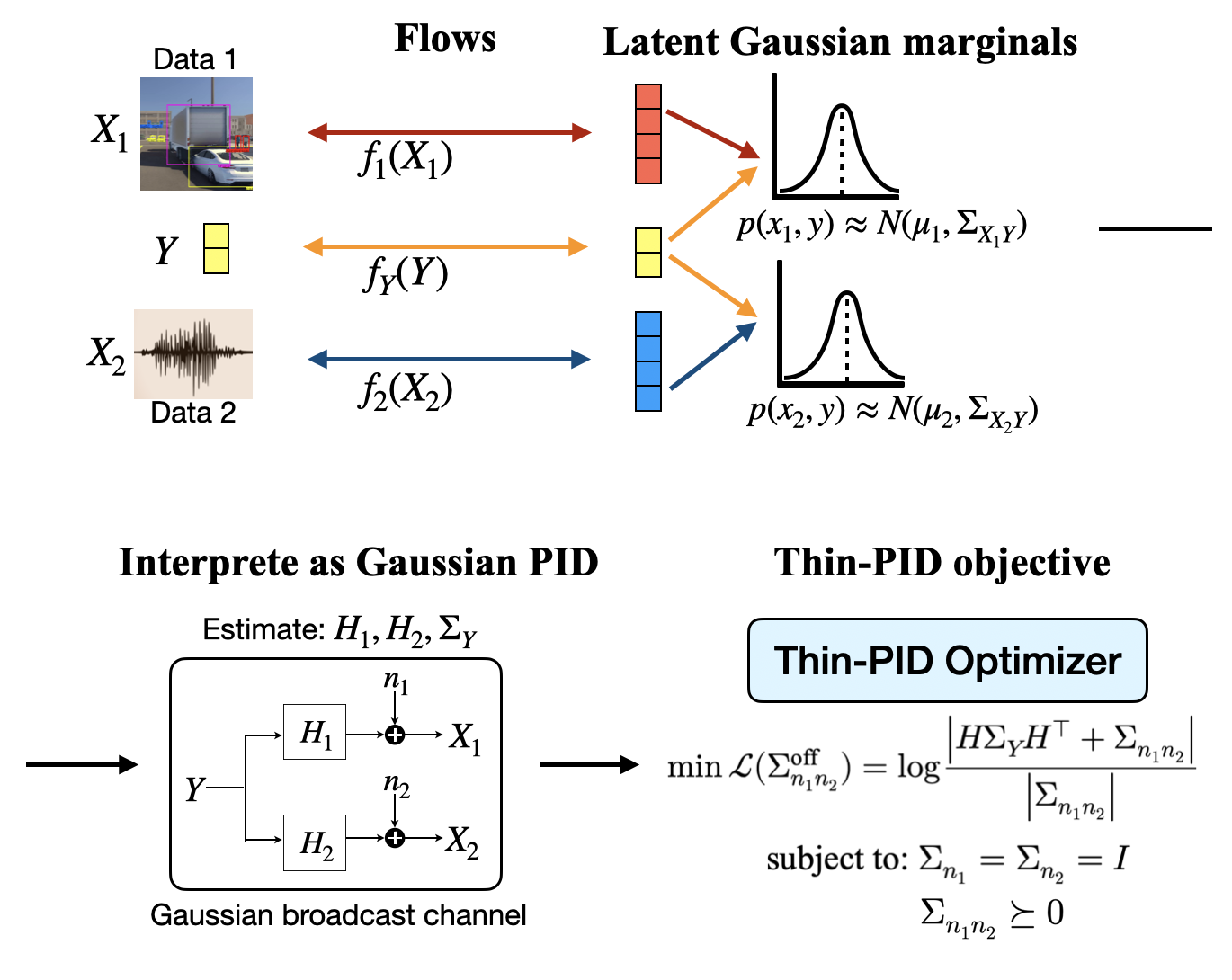
-
Gaussian Processes meet Deep Neural Networks
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are powerful tools capable of capturing intricate patterns in large datasets, but lack the ability to provide uncertainty estimation. To learn rich, hierarchical representations from data with proper interpretability and uncertainty estimation, we explore the integration of DNNs with Gaussian Processes (GPs), leading to Deep Kernel Learning (DKL) and Deep Gaussian Processes (DGPs).
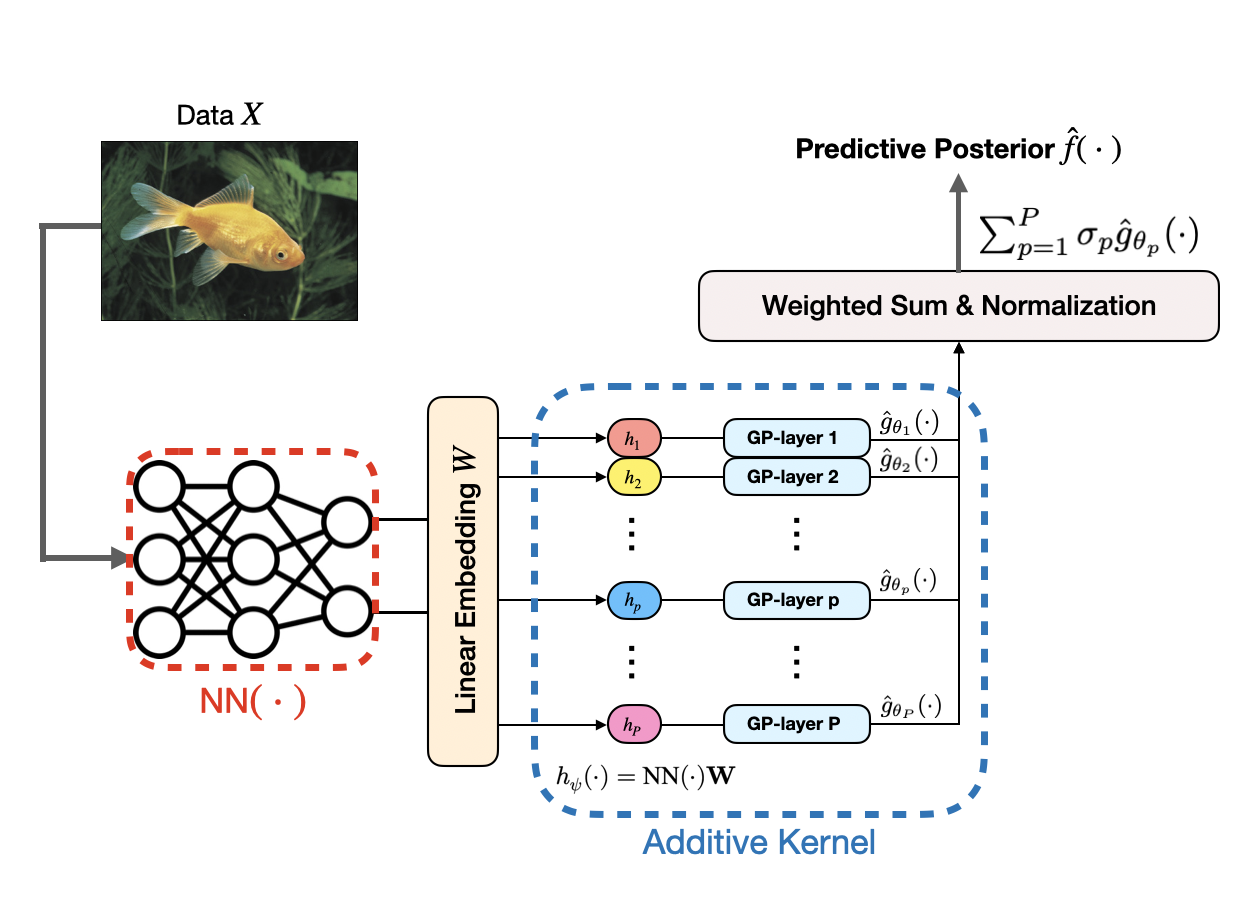
-
Private Information Retrieval
Private information retrieval (PIR) systems are motivated by the necessity to safeguard user privacy during information retrieval. In the canonical PIR framework, a user wishes to retrieve a message from N independent servers, each holding a complete set of K messages. The message’s identity must remain hidden from any individual server. This privacy requirement necessarily incurs higher download costs than a protocol without such a requirement, which requires effort to improve the code construction of PIR systems.
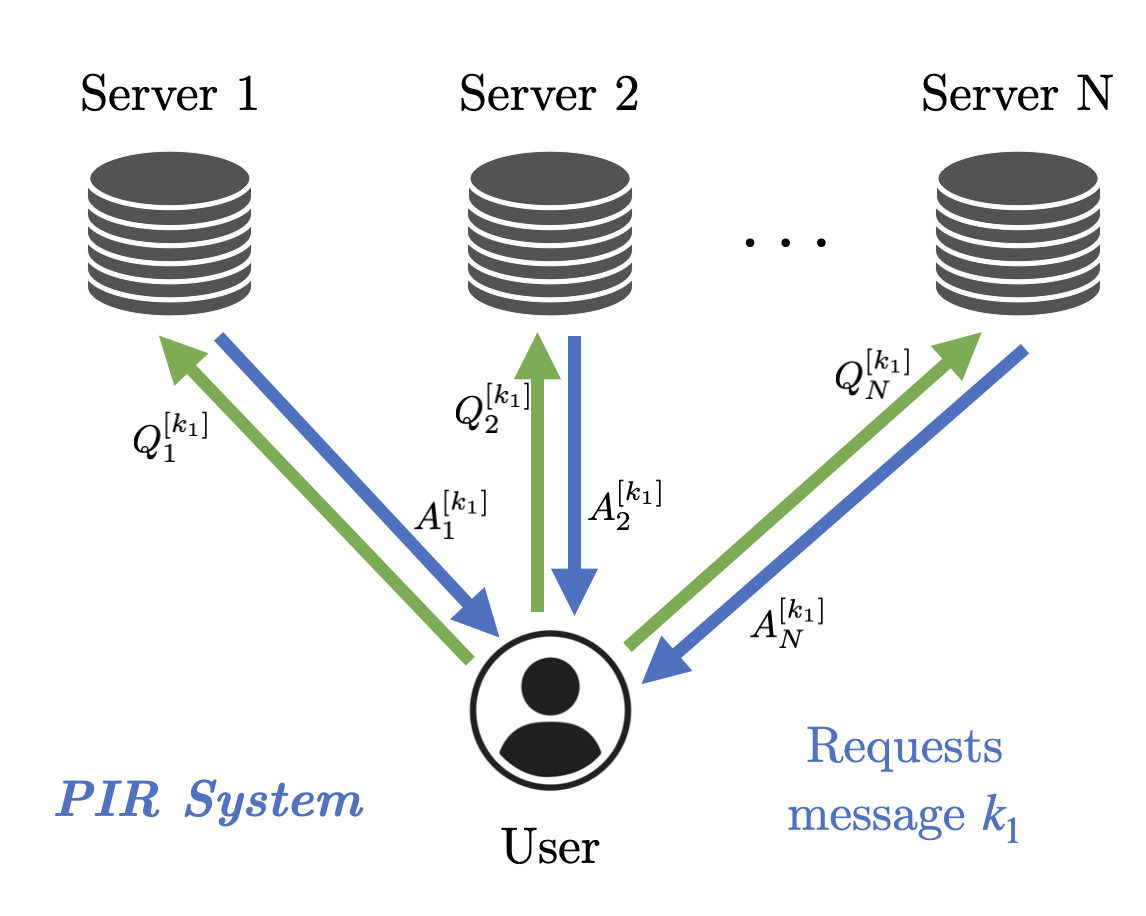
-
AI-driven Dynamic mmWave Networking
Integrated Access and Backhaul (IAB) is an emerging technique to enable cost-effective deployment of dense 5G networks that utilize emerging millimeter-wavelength (mmWave) spectrum. Existing heuristic-based network control/management frameworks are not well-suited for the increasing complexity and uncertainty introduced by mmWave IAB. Machine learning (ML) can help automate network control decisions, but its practical deployment faces new system-level challenges in 5G IAB, including accurate simulation-based training, resolving conflicting objectives from heterogeneous network slices, and efficiently collecting observations for run-time decision-making.

-
Machine Learning Projects
Related projects in machine learning and data science. ML-based customer review classifier. A complex-valued gradient neural network (CVGNN) to solve the Moore-Penrose inverse of complex matrices. Fog computing in the Internet of Vehicles (IoV).